INTRODUCTION TO RADAR
Nowadays communication plays an important role in the world. Suppose if we want to communicate with a person who is far away it is possible with the help of communication devices. The communication devices in the sense, it consisting of Source, Transmitter, channel(Medium), Receiver, Destination. For example, if we want to transmit information in the sense generally voice can be first converted into electrical signals by the help of ADC's(analog to digital converters) usually, voice signals which we have to transmit are very low frequencies so that if we transmit these signals directly with the help of transmitter will undergo some losses in the sense the original signal(voice signal) can be attenuated. Therefore, in order to transmit the original signals without any distortions, we are going to the new concept that is Modulation. Modulation is nothing but "the process of combining the original message signal with a high-frequency carrier signal in the order of few Megha hedges. Therefore the main advantage of modulation is to reduce the height of the antenna with great power handling so that we can transmit the message the signals to long distances.
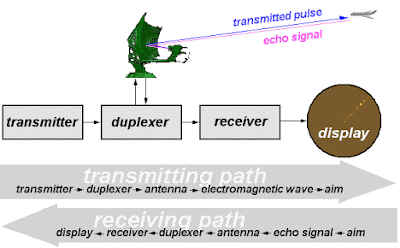
The expansion of RADAR is Radio Detection And Ranging.RADAR is an object-detection system that uses radio Waves to determine the range, angle, or velocity of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, space crafts, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formation, and terrain. A radar system consists of transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwave domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna to accept or capture the electromagnetic signals in the same direction of the transmitted signal, a receiver, and processor to determine properties of the object(target).
RADAR PRINCIPLE:-
As mentioned in the above with the help of the RADAR system we can find out the
1.The velocity of the target,
2.The direction of the target,
3. Location of the target, and
4. The Range of the target.
RADAR is an echo ranging system in which the transmitter produces pulses of radio waves in the range of 150MHZ to 30GHZ of very-high-power generated pulses is given to the duplexer. Duplexer consists of two switches. they are :
- TR switch[Transereceiver switch], and
- ATR switch[Anti Transceiver switch].
figure: RADAR block diagram.
figure: Interaction with the target.
The Duplexer is a switch, which connects the transmitter or receiver to the antenna alternately. During the transmission time, the switch ATR is connected to the antenna. The pulse completed from the transmitter, the duplexer disconnects the transmitter and connect the antenna to the receiver. Now the receiving antenna receives the echo signal and given to the output devices like display units. There are different types of displays used in RADAR, they are :
1.A-scope,
2.B-scope,
3.C-scope, and
4.PPI.
By the help of these displays, we can find out the velocity of the target, the direction of the target, the location of the target and range of the target.
PRINCIPLE:-
The basic principle of CWRADAR (Continuous radar) depends upon doppler effect. Doppler effect is widely used in RADAR to detect the target, where the target is located at the visible distance to us. Doppler effect means an apparent(change) shift in the frequency between the RADAR and target. Example: Sound of a whistle from the passing train. It can be explained by the three cases. They are :
Case-1:- If the target is nearer to the RADAR station, the frequency is increased.i.e, ft+FD.
Case-2:- If the target is away from the RADAR station, the frequency is decreased.i.e,ft-FD.
Case-3:- If the object is stationary, then the frequency is constant.
Therefore Dopler frequency shift is given by, FD = 2vr/(lambda).
Where, FD= Dopler shift frequency,
vr= Velocity of the target with respect to radar.
Case-2:- If the target is away from the RADAR station, the frequency is decreased.i.e,ft-FD.
Case-3:- If the object is stationary, then the frequency is constant.
Therefore Dopler frequency shift is given by, FD = 2vr/(lambda).
Where, FD= Dopler shift frequency,
vr= Velocity of the target with respect to radar.

No comments:
Post a Comment